Segmentation and Targeting in B2B Marketing: A Comprehensive Guide
Orange Owl
March 17, 2025

Table of Contents
Introduction
In the ever-evolving landscape of B2B marketing, understanding your audience is key to success. Unlike B2C marketing, where broad consumer categories can be targeted, B2B marketing requires a more refined approach. Businesses operate with different goals, structures, and decision-making processes, making it essential to segment and target audiences strategically. Market segmentation and targeting are foundational strategies in B2B marketing, enabling companies to tailor their approaches to specific groups based on shared characteristics. One prevalent method is firmographic segmentation, which involves categorizing businesses based on industry, company size, location, and more attributes. Notably, 81% of B2B marketers utilize firmographic segmentation to enhance their targeting efforts. Effective segmentation enables companies to tailor their messaging, optimize resources, and improve lead-generation efforts, ultimately driving sales and fostering long-term relationships.
This guide delves deep into segmentation and targeting in b2b marketing.
What is Segmentation in B2B Marketing?
Segmentation in B2B marketing involves dividing a large and diverse business market into smaller, more defined segments based on common characteristics. The goal is to identify groups of potential customers who share similar needs, behaviors, or pain points. By categorizing customers into specific groups, businesses can create personalized marketing campaigns, improve engagement, and increase conversion rates.
Key Benefits of Segmentation in B2B Marketing:
- Improved Marketing Efficiency: By focusing on specific segments, businesses can tailor their strategies, improving engagement and ROI.
- Personalization: Helps in crafting more relevant messaging that resonates with the target audience.
- Better Resource Allocation: Companies can allocate marketing budgets effectively by targeting the most profitable segments.
- Increased Competitive Advantage: A well-segmented market strategy allows businesses to differentiate themselves from competitors.
- Higher Conversion Rates: Tailored solutions and targeted campaigns lead to better conversion rates and stronger customer relationships.
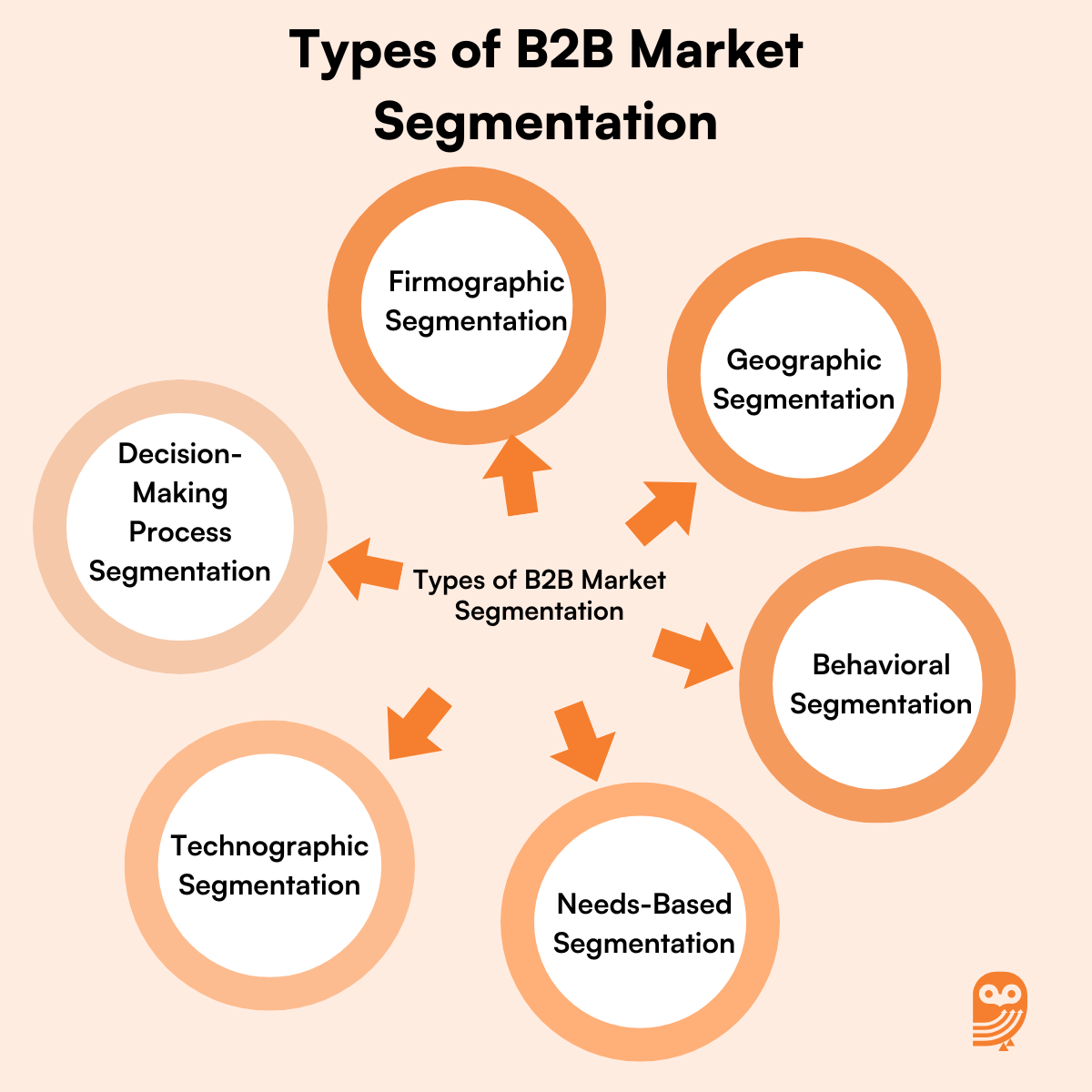
Types of B2B Market Segmentation
B2B segmentation can be categorized into several key types:
1. Firmographic Segmentation
Firmographics are the B2B equivalent of demographics. This segmentation type classifies businesses based on characteristics such as:
- Industry type (Technology, Healthcare, Manufacturing, etc.) – For example, a cloud computing company might segment its audience into fintech, healthcare, and retail industries to tailor its messaging accordingly.
- Company size (Startups, SMEs, Large Enterprises) – A SaaS company offering HR software might create different versions of its product to cater to small businesses and large enterprises.
- Revenue – Companies with different revenue levels may have varying budgets and purchasing behaviors.
- Location – A logistics provider may segment clients based on whether they operate locally, nationally, or internationally.
- Growth stage (Emerging, Established, Market Leader) – A software development firm might target early-stage startups differently than well-established enterprises.
2. Geographic Segmentation
Businesses may have different needs based on their geographic location. This segmentation includes:
- Country or region – Companies selling industrial machinery might have different strategies for North America versus Southeast Asia due to regulatory and economic differences.
- Urban vs. rural markets – A B2B telecom provider may offer different packages to businesses in metropolitan areas compared to rural regions.
- Local regulations and policies – A pharmaceutical supplier might tailor its approach based on the specific regulatory requirements in different countries.
- Climate or economic conditions – Construction material suppliers may segment clients based on climate conditions affecting building materials.
3. Behavioral Segmentation
This type of segmentation focuses on customer behaviors and interactions, including:
- Purchase history – A software provider might offer loyalty discounts to businesses that renew their subscriptions annually.
- Brand loyalty – Businesses that frequently engage with a brand’s content or services may receive exclusive offers.
- Product usage patterns – A cloud storage company might segment users based on data storage needs and recommend upgrades accordingly.
- Response to marketing campaigns – Tracking engagement metrics such as email opens or webinar attendance helps in refining future campaigns.
- Customer engagement level – Companies engaging frequently with a brand’s webinars, whitepapers, or consultations might be targeted for premium services.
4. Needs-Based Segmentation
Businesses have different needs based on their pain points and objectives. Segmentation based on needs helps in crafting solutions tailored to specific business challenges. For example:
- A cybersecurity firm may target companies concerned about compliance regulations differently than those focused on securing remote work environments.
- An enterprise software provider might develop different solutions for cost reduction and operational efficiency versus innovation and scalability.
- A logistics provider may offer customized solutions for businesses that prioritize cost savings versus those emphasizing fast deliveries.
5. Technographic Segmentation
With the rise of digital transformation, companies increasingly segment their B2B audiences based on technology use, including:
- Software and tools used – A digital marketing agency might tailor its services differently for companies using HubSpot versus those using Salesforce.
- IT infrastructure – A cloud services provider may target businesses using on-premise servers differently than those already using cloud solutions.
- Digital maturity level – Companies with high digital adoption may be open to automation solutions, while traditional businesses might need more education and consultation.
- Cybersecurity needs – Companies with a remote workforce might require stronger endpoint security solutions compared to businesses with centralized operations.
6. Decision-Making Process Segmentation
Different companies have different decision-making structures. Understanding who makes purchasing decisions—whether it’s a single decision-maker, a committee, or a group of stakeholders—helps in targeted marketing efforts. For example:
- A business selling corporate training programs may segment organizations where HR makes the decision versus those where department heads or CEOs have the final say.
- A supplier of industrial equipment may create separate strategies for businesses where procurement teams handle purchases versus those where CFOs oversee spending decisions.
- A SaaS company selling enterprise solutions may target CTOs and CIOs differently than companies where department managers influence decisions.
Strategic Impact of B2B Segmentation
Market segmentation is not just a classification exercise—it’s a powerful growth strategy. Businesses that leverage effective segmentation see:
✅ Higher lead-to-customer conversion rates
✅ More efficient marketing spend allocation
✅ Stronger brand positioning and customer retention
✅ Increased sales and revenue growth
By adopting a data-driven approach to segmentation—whether through firmographics, technographics, or behavioral insights—you can refine your marketing and sales strategies for sustainable success in the B2B landscape.
Targeting in B2B Marketing
Once segmentation is complete, the next step is targeting—selecting the most suitable segment to market to. Targeting involves assessing the potential profitability, accessibility, and responsiveness of each segment and prioritizing them based on business objectives.
Why Targeting Matters in B2B Marketing?
B2B buyers are highly specific in their needs and decision-making processes. A well-defined targeting strategy ensures that your marketing efforts are focused on the most relevant prospects, leading to:
- Higher conversion rates
- Better resource allocation
- Increased customer retention
- Stronger brand positioning
Steps in Effective Targeting:
- Evaluate Market Segments: Analyze the potential of each segment in terms of size, profitability, and fit with your product or service.
- Select the Right Target Segment: Choose the segments that align best with your business capabilities and market positioning.
- Develop a Positioning Strategy: Create compelling messaging that resonates with the selected segment.
- Customize Marketing Campaigns: Use the insights from segmentation to design personalized marketing strategies.
Key Strategies for Effective B2B Targeting
1. Define Your Ideal Customer Profile (ICP)
An Ideal Customer Profile helps you identify businesses that are the best fit for your product or service. Factors to consider include:
- Industry
- Company size
- Revenue
- Geographic location
- Technology stack
- Pain points and challenges
2. Segment Your Market
Segmentation allows businesses to tailor their messaging and offers to specific groups. Common B2B segmentation strategies include:
- Firmographic Segmentation – Based on company attributes like size, industry, and revenue.
- Behavioral Segmentation – Based on user interactions, engagement, and purchasing history.
- Needs-Based Segmentation – Focused on the specific pain points or requirements of the customer.
- Tiered Segmentation – Prioritizing high-value accounts over lower-priority prospects.
3. Leverage Account-Based Marketing (ABM)
ABM is a highly personalized approach where marketing and sales teams collaborate to target high-value accounts. It involves:
- Identifying key decision-makers within target accounts
- Crafting personalized marketing campaigns
- Engaging prospects through multiple touchpoints
4. Utilize Data and Analytics
Data-driven targeting improves precision and effectiveness. Businesses can leverage:
- CRM data for customer insights
- Website analytics to understand visitor behavior
- Predictive analytics to identify high-potential leads
5. Optimize Your Digital Marketing Channels
Targeting works best when combined with the right digital marketing channels. Key channels include:
- LinkedIn Ads – Best for reaching B2B professionals and decision-makers.
- Google Ads – Target specific search queries and display relevant ads.
- Content Marketing – Create industry-specific blogs, case studies, and whitepapers to attract qualified leads.
- Email Marketing – Nurture leads with personalized email campaigns.
6. Align Sales and Marketing Efforts
Successful targeting requires seamless collaboration between marketing and sales teams. Regular communication, shared insights, and unified strategies ensure better lead nurturing and conversion.
Conclusion
B2B marketing success hinges on effective segmentation and targeting. By categorizing businesses into well-defined segments, companies can craft tailored marketing strategies that maximize engagement and conversion rates. Understanding customer needs, behaviors, and decision-making processes enables businesses to deliver personalized experiences, build trust, and foster long-term relationships. A strategic approach ensures businesses reach the right audience with the right message, ultimately driving growth, improving ROI, and creating a sustainable competitive advantage in the marketplace.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on Segmentation and Targeting in B2B
B2B market segmentation is the process of dividing a broad business market into distinct groups based on shared characteristics such as industry, company size, location, and buyer behavior.
Importance:
- Better Targeting: Helps in crafting personalized marketing messages.
- Efficient Resource Allocation: Ensures marketing efforts are focused on high-value prospects.
- Improved Conversion Rates: Tailored strategies increase engagement and lead generation.
- Competitive Advantage: Enables businesses to differentiate themselves by addressing specific customer needs.
B2B segmentation can be categorized into the following types:
- Firmographic Segmentation: Based on company characteristics like industry, size, revenue, and location.
- Demographic Segmentation: Targets decision-makers based on job title, seniority, and department.
- Behavioral Segmentation: Focuses on customer interactions, purchase behavior, and brand loyalty.
- Geographic Segmentation: Divides markets by country, region, or city to align with local demand.
- Technographic Segmentation: Groups companies based on the technology stack they use.
- Needs-Based Segmentation: Identifies businesses based on specific pain points and requirements.
Choosing the right segmentation method depends on business goals and target audience preferences.
B2B targeting differs from B2C in several key aspects:
- Audience Complexity: B2B involves multiple decision-makers, whereas B2C targets individuals.
- Sales Cycle: B2B purchases take longer due to higher-value transactions and complex negotiations.
- Content & Messaging: B2B marketing focuses on logic, ROI, and problem-solving, while B2C appeals to emotions and impulse buying.
- Advertising Channels: B2B marketing leverages LinkedIn, email, and account-based marketing (ABM), whereas B2C relies more on social media and direct-to-consumer advertising.
Understanding these differences helps businesses create more effective segmentation and targeting strategies.
To target B2B buyers effectively, businesses should:
- Define Ideal Customer Profiles (ICPs): Identify company size, industry, revenue, and challenges.
- Use Account-Based Marketing (ABM): Personalize marketing for high-value accounts.
- Leverage Data & Analytics: Use CRM and marketing automation tools to refine targeting.
- Implement Multi-Channel Strategies: Use LinkedIn Ads, Google Ads, email marketing, and direct outreach.
- Optimize Content for Decision-Makers: Provide case studies, whitepapers, and ROI-driven content.
Firmographic segmentation categorizes businesses based on key company attributes, improving marketing efficiency by:
- Enhancing Personalization: Messages can be tailored based on industry, company size, and growth stage.
- Improving Lead Scoring: Helps prioritize high-value prospects based on revenue and employee count.
- Optimizing Ad Spend: Ensures PPC and LinkedIn campaigns reach the most relevant companies.
- Facilitating Account-Based Marketing: Enables hyper-focused targeting for enterprise accounts.
By leveraging firmographic data, businesses can refine their outreach and maximize marketing ROI.
Account-Based Marketing (ABM) is a focused approach where businesses create personalized marketing campaigns for specific high-value accounts.
ABM Benefits:
- Higher Engagement: Personalized content increases response rates.
- Improved Sales Alignment: Marketing and sales teams collaborate to close deals faster.
- Better ROI: Focused efforts lead to higher conversion rates and larger deal sizes.
- Stronger Customer Relationships: Customized outreach fosters trust and long-term partnerships.
ABM works best for B2B companies with high-ticket products and services that require complex decision-making processes.
Behavioral segmentation classifies prospects based on their interactions with your brand. This includes:
- Website Behavior: Tracking pages visited, content downloaded, and time spent on site.
- Email Engagement: Monitoring open rates, click-through rates, and responses.
- Purchase History: Analyzing past transactions and contract renewals.
- Event Participation: Segmenting leads based on webinar attendance or conference participation.
Using behavioral insights, businesses can personalize follow-ups, nurture leads effectively, and improve conversion rates.
Technology enables businesses to segment and target B2B customers more accurately through:
- CRM Systems (e.g., Salesforce, HubSpot): Store and analyze customer data.
- Marketing Automation (e.g., Marketo, Pardot): Personalize email and ad campaigns.
- Data Analytics Tools (e.g., Google Analytics, Power BI): Track customer behavior and refine targeting.
- AI & Machine Learning: Predict customer intent and optimize segmentation strategies.
- Social Media & Ad Platforms (e.g., LinkedIn, Google Ads): Offer precise targeting based on industry, job title, and company attributes.
By leveraging these technologies, B2B marketers can create more efficient and scalable segmentation strategies.
Key metrics to measure segmentation and targeting success include:
- Conversion Rates: Measure how many targeted leads turn into customers.
- Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC): Evaluate the cost of acquiring new customers through segmented campaigns.
- Lead Quality Score: Assess how well segmented leads match your Ideal Customer Profile.
- Engagement Metrics: Monitor email open rates, ad click-through rates, and content downloads.
- Sales Cycle Length: Analyze whether targeted efforts shorten the decision-making process.
Regularly reviewing these metrics ensures that segmentation efforts are delivering the desired results.
Some common mistakes in B2B segmentation and targeting include:
- Over-Segmentation: Narrowing the target audience too much, limiting lead volume.
- Ignoring Data Insights: Making decisions without leveraging analytics.
- Lack of Personalization: Sending generic messages instead of tailored content.
- Failing to Update Segments: Not refining audience segments based on new customer behavior.
- Relying on a Single Channel: Using only one marketing channel instead of a multi-channel approach.
Avoiding these mistakes helps businesses refine their segmentation strategy and improve marketing efficiency.


