Freemium vs. Free Trial: A Comprehensive Guide for B2B SaaS Companies
Orange Owl
June 16, 2025

Table of Contents
Introduction
In the competitive landscape of B2B SaaS, choosing the right approach to attract and convert potential customers is crucial for success. Freemium and free trial models are popular strategies for user acquisition and conversion, but deciding which approach—or whether to use both—can be challenging. This comprehensive guide will explore the nuances of each model, provide best practices and examples, and offer guidance on choosing the right strategy for your business.
Understanding Freemium Vs. Free Trial Models
Before diving into the details, it’s important to understand what freemium and free trial models entail and how they function in the context of B2B SaaS.
Freemium Model
The freemium model offers a basic version of the product for free, with the option to upgrade to a paid plan for additional features and benefits. This approach lowers the barrier to entry, allowing users to experience the product without any financial commitment. The goal is to convert free users into paying customers by demonstrating the value of premium features over time.
Key Characteristics of Freemium:
- Indefinite Access: Users can access the free version indefinitely, providing ongoing opportunities for engagement and conversion.
- Limited Features: The free version typically includes essential features, while premium features are reserved for paid plans.
- Large User Base: Freemium attracts a large number of users, increasing brand visibility and market penetration.
Free Trial Model
The free trial model provides full access to the product for a limited period, allowing users to explore all features before deciding to purchase. This approach targets users who are ready to evaluate the product and make a purchasing decision quickly.
Key Characteristics of Free Trial:
- Time-Limited Access: Users have full access to the product for a set period, typically ranging from 7 to 30 days.
- Full Feature Access: Users can experience the complete functionality of the product, allowing for thorough evaluation.
- Quick Conversion: The trial period creates urgency for users to decide whether to purchase before their access expires.
Advantages and Challenges of Each Model
Freemium Model: Pros, Cons, and Considerations
Pros:
- User Engagement: Freemium encourages continuous user engagement without time pressure, leading to higher user satisfaction and retention.
- Brand Awareness: The model helps build brand recognition by attracting a large number of users, who can spread the word through organic referrals.
- Lower Customer Acquisition Costs: Freemium can reduce marketing and acquisition costs by leveraging word-of-mouth and organic growth.
- User Feedback and Data Collection: A large user base provides valuable feedback and data, which can inform product improvements and development.
Cons:
- Low Conversion Rates: Freemium typically has lower conversion rates compared to free trials, with many users satisfied with the free version.
- High Maintenance Costs: Supporting a large base of free users can strain resources, impacting customer support and infrastructure costs.
- Value Perception: If the free version is too generous, users may perceive less value in upgrading to premium plans.
- Market Suitability: The model requires a large target market to be sustainable, making it less suitable for niche products.
Considerations:
- Ensure that your target market is large enough to support a freemium model.
- Evaluate whether the freemium model aligns with your growth strategy, especially if focusing on long-term user engagement.
- Consider using a combination of feature limitations and usage caps to balance user experience and encourage upgrades.
Free Trial Model: Pros, Cons, and Considerations
Pros:
- High Conversion Rates: Free trials generally have higher conversion rates as users experience the full product value upfront.
- Quality Leads: The model attracts more qualified leads, as users are actively seeking solutions and are more likely to convert after experiencing the product.
- Urgency and Engagement: The time-limited nature creates a sense of urgency, driving users to engage with the product intensively during the trial period.
- Clear Monetization Path: The trial model offers a straightforward path from trial to subscription, simplifying the sales process.
Cons:
- Limited User Base: Free trials may attract fewer sign-ups compared to freemium, as users are less inclined to commit to time-limited access.
- Pressure to Convert: The short trial period may deter users who need more time to evaluate the product’s value fully.
- Resource Allocation: Requires strong sales and customer support teams to nurture leads and convert trial users.
- Trial Abandonment: Users may disengage if the onboarding process is complicated or if they do not quickly realize the product’s value.
Considerations:
- Assess whether your product’s value is easily demonstrable within the trial period.
- Implement effective onboarding and engagement strategies to maximize the trial experience.
- Consider extending the trial period or offering personalized demos to cater to users who need more time.
Exploring Different Freemium Models
Freemium models can vary in terms of feature access and usage limitations. Here are common approaches to structuring freemium plans:
1. Feature-Limited Freemium
Description:
Users have access to a limited set of features for free, with the option to upgrade to access additional functionalities.
Example:
Slack offers a free plan with basic messaging and collaboration tools. To access advanced features like unlimited integrations and usage history, users must upgrade to a paid plan.
Pros:
- Encourages exploration of core features.
- Incentivizes upgrades by highlighting the value of premium features.
Cons:
- Limited feature access may not demonstrate full product value.
2. Usage-Limited Freemium
Description:
Users have access to all features, but with limitations on usage, such as the number of projects, users, or data storage.
Example:
Trello allows users to create unlimited boards and cards for free but limits the number of Power-Ups (integrations) and file attachments. Paid plans remove these limitations.
Pros:
- Demonstrates full product capabilities.
- Motivates users to upgrade as their needs grow.
Cons:
- Usage limitations may frustrate users as they reach their limits.
3. Time-Limited Freemium
Description:
Users have full access to all features for a limited period, after which they revert to a free plan with restricted features.
Example:
Dropbox offers a 30-day trial of Dropbox Business, providing full feature access. After the trial, users can continue with a free plan or upgrade to a paid subscription.
Pros:
- Provides comprehensive product experience.
- Creates urgency for users to evaluate and decide.
Cons:
- Limited time may not be sufficient for users to fully appreciate the value.
Comparing Freemium Vs. Free Trial Models
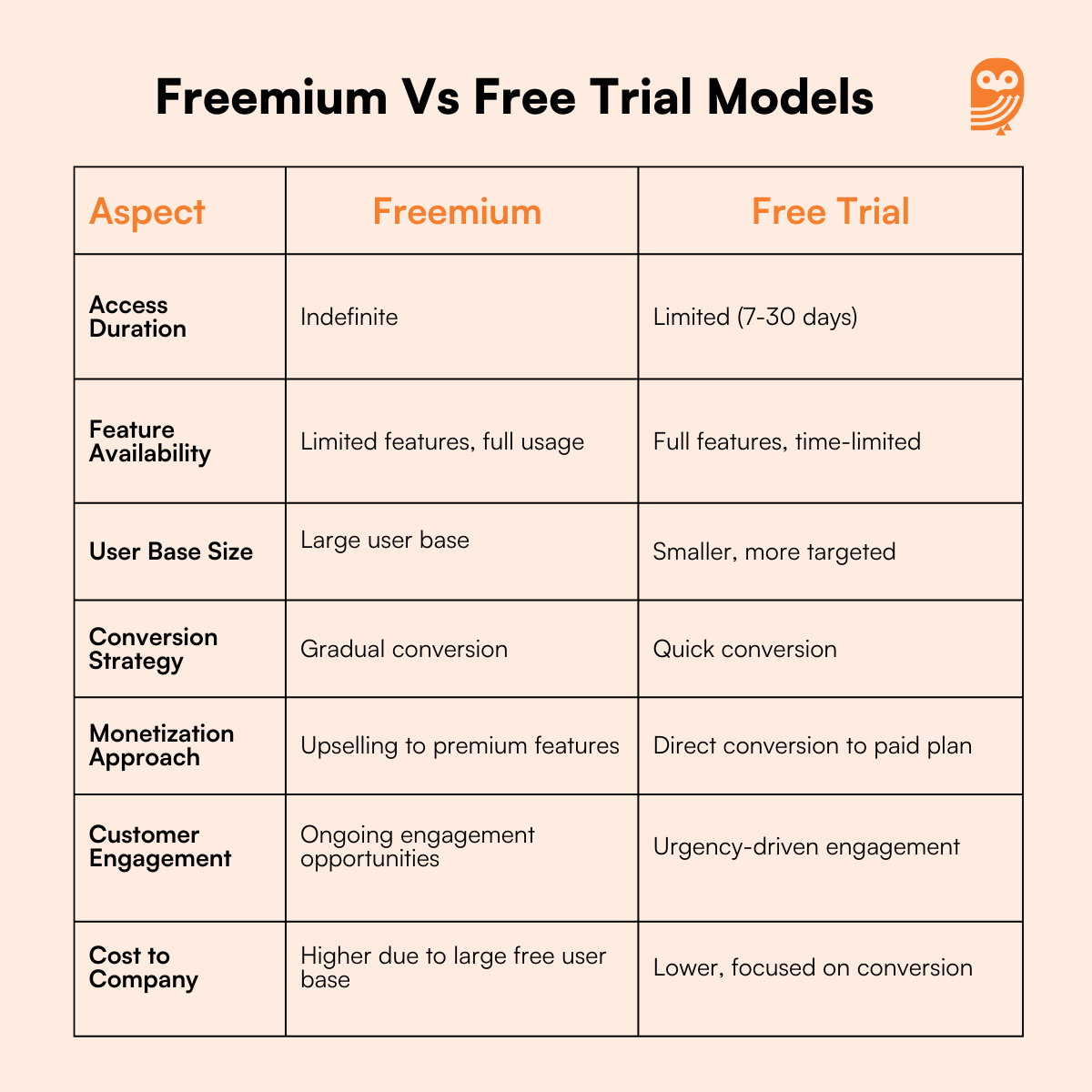
Choosing the Right Model for Your B2B SaaS Company: Freemium Vs. Free Trial
Selecting the right model depends on various factors, including your target audience, product complexity, and business goals. Here are steps to guide your decision:
Step 1: Understand Your Audience
- Analyze Needs: Identify your target audience’s needs, preferences, and behavior. Understand whether they prefer exploring features over time or need a comprehensive evaluation upfront.
- Assess Willingness to Pay: Determine how much value potential customers place on your product and their willingness to pay for premium features.
Step 2: Evaluate Product Complexity
- Feature-Rich Products: If your product has a steep learning curve or requires in-depth exploration, a freemium model may be more suitable to allow users time to discover value.
- Straightforward Products: For products with clear, immediate value, a free trial can provide users with a full experience and encourage quick conversion.
Step 3: Align with Business Goals
- Brand Awareness: If your goal is to build brand awareness and capture a large user base, a freemium model can help achieve this by lowering the entry barrier.
- Revenue Growth: If immediate revenue growth is a priority, a free trial may lead to faster conversions and monetization.
Step 4: Consider Resource Allocation
- Support and Infrastructure: Evaluate your ability to support a large base of free users in a freemium model. Ensure you have the resources to provide quality support and maintain infrastructure.
- Conversion and Sales: Consider your sales strategy and how well-equipped your team is to handle leads and conversions from a free trial model.
Step 5: Test and Iterate
- Conduct Experiments: Implement both models in controlled experiments to assess their impact on user acquisition, engagement, and conversion. Analyze data to refine your approach.
- Gather Feedback: Collect feedback from users and sales teams to understand the effectiveness of each model and identify areas for improvement.
Real-World Success Stories: Freemium Vs. Free Trial in Action
Freemium Success Stories
- Mailchimp: Offers a freemium plan with limited features and usage caps. This model allows users to explore the platform’s capabilities and upgrade as their needs grow.
- Slack: Provides a freemium version with essential features for team communication, encouraging users to upgrade for additional integrations and support.
Free Trial Success Stories
- Intercom: Utilizes a 14-day free trial to showcase its customer support and engagement platform, leading to higher conversion rates.
- Adobe Creative Cloud: Offers a 7-day free trial, allowing users to experience the full suite of creative tools, which drives conversions to paid subscriptions.
How to Optimize Your Chosen Model
Freemium Optimization Strategies
- Limit Features Wisely: Balance between offering enough value to engage users and enticing them to upgrade.
- Leverage In-App Prompts: Use notifications and reminders to highlight premium features and encourage upgrades.
- Build a Community: Foster user engagement and organic referrals by building a strong user community.
Free Trial Optimization Strategies
- Effective Onboarding: Guide users through the product with tutorials and personalized support to maximize trial engagement.
- Create Urgency: Use countdown timers and reminders to encourage users to make a purchase decision before the trial ends.
- Collect Feedback: Gather insights from trial users to identify barriers to conversion and refine your approach.
Combining Freemium and Free Trial Models
Some B2B SaaS companies successfully combine freemium and free trial models to capture different segments of their target audience. Here’s how they do it:
- Freemium as a Gateway: Use the freemium model to attract a wide user base, offering basic features for ongoing engagement. This approach builds brand awareness and user familiarity.
- Free Trial for Quick Wins: Offer a free trial of premium features to encourage users who are ready to explore the full product. This strategy targets users likely to convert quickly.
Example:
Canva uses a combined approach. They offer a free plan with essential design tools and a 30-day free trial of Canva Pro, allowing users to explore advanced features before committing to a subscription.
Best Practices for Implementing Freemium and Free Trial Models
Here are some best practices and expert tips for implementing these models effectively:
Freemium Best Practices
- Define Clear Upgrade Paths: Clearly outline the benefits of upgrading to a premium plan. Highlight specific features or services that offer enhanced value.
- Provide In-App Prompts: Use in-app prompts and notifications to remind users of premium features and encourage upgrades based on their usage patterns.
- Offer Tiered Plans: Consider offering multiple premium plans to cater to different user needs and budgets, providing flexibility in upgrading.
Free Trial Best Practices
- Onboard Effectively: Provide a seamless onboarding experience during the trial period, with tutorials and personalized support to help users understand the product.
- Create Urgency: Use countdown timers and reminders to create urgency and encourage users to make a decision before the trial ends.
- Collect Feedback: Gather feedback from trial users to understand their experience and address any concerns that may hinder conversion.
Common Pitfalls and How to Avoid Them
- Overcomplicating the Free Version: Offering too many features in the free version can reduce the incentive to upgrade.
- Short Trial Periods: Insufficient trial durations may prevent users from experiencing the product’s full value.
- Neglecting User Support: Providing inadequate support to free users can lead to poor user experiences and high churn rates.
- Misjudging Target Audience: Failing to align the model with user expectations can result in low conversion rates.
How to Know if Your Strategy is Working
Measuring the success of your chosen model is crucial for ongoing optimization. Here are key metrics to track:
- Conversion Rates: Monitor the percentage of users who convert from free to paid plans. Analyze factors influencing conversion, such as feature usage and engagement levels.
- User Engagement: Track user activity and engagement within the product. High engagement often correlates with a higher likelihood of conversion.
- Churn Rates: Measure churn rates to identify retention challenges. High churn may indicate issues with product value or user experience.
- Revenue Growth: Evaluate revenue growth from conversions and upsells. Consider both immediate and long-term impacts on your bottom line.
- Customer Feedback: Collect and analyze feedback from users to identify strengths and areas for improvement in your approach.
Conclusion
Choosing between freemium and free trial models—or using both—requires careful consideration of your product, audience, and business objectives. By understanding the strengths and challenges of each model, you can tailor your strategy to effectively attract and convert customers in the competitive B2B SaaS landscape. Continuously monitor performance
Frequently Asked Questions on Freemium Vs. Free Trial Models
The Freemium model can lower CAC by attracting a larger user base through word-of-mouth and organic referrals. It reduces upfront marketing expenses as users can experience the product without cost, driving brand awareness and engagement.
However, maintaining a large free user base can lead to higher support and infrastructure costs. Conversely, the Free Trial model targets more qualified leads, potentially lowering CAC by focusing on users who are actively seeking solutions. It requires investment in sales and customer support to nurture leads, but successful trials can lead to quicker conversions and a more predictable revenue stream.
Effective user onboarding is crucial for both freemium and free trial models, as it helps users quickly understand the product’s value and encourages engagement. For freemium users, onboarding should focus on guiding them through key features, encouraging exploration, and highlighting premium benefits.
For free trial users, onboarding should be time-sensitive, showcasing product capabilities and demonstrating value within the trial period. Personalized support, tutorials, and interactive walkthroughs can enhance user experience, leading to higher conversion rates and customer satisfaction.
.
Balancing free and paid features in a freemium model involves offering enough value to engage users while incentivizing them to upgrade. Companies should focus on providing essential features that showcase the product’s core value in the free version.
Premium features should offer enhanced functionality, integrations, and support that address specific pain points or advanced use cases. Regularly analyze user behavior and feedback to adjust feature offerings, ensuring that the free version is compelling but not too generous to discourage upgrades.
Common pitfalls in the freemium model include offering too many features for free, which can reduce the incentive to upgrade. Companies may also face challenges in supporting a large base of non-paying users, leading to resource strain. Failing to communicate the value of premium features or neglecting user engagement and support can hinder conversions.
To avoid these pitfalls, SaaS companies should carefully design their free offering, maintain a balance between free and premium features, and actively engage users through targeted marketing and support efforts.
Freemium models can enhance customer retention by providing ongoing engagement opportunities, leading to higher CLTV as users upgrade over time. However, the model requires consistent user value delivery and engagement to prevent churn. Free trial models create urgency and focus on quick conversions, potentially leading to higher initial retention rates.
However, maintaining retention post-trial requires delivering consistent value and support to ensure continued satisfaction. Both models require strategies to nurture customer relationships, encourage upsells, and maximize CLTV.
SaaS companies can measure the success of their freemium or free trial model by tracking key metrics such as conversion rates, user engagement, and churn rates. For freemium models, focus on the percentage of free users who convert to paying customers, as well as engagement metrics like active usage and feature adoption.
For free trials, measure trial-to-paid conversion rates, time-to-conversion, and trial abandonment rates. Collecting user feedback and analyzing usage patterns can provide insights into user behavior and identify areas for improvement in the acquisition process.
.
To effectively transition from a freemium model to a paid model, companies should communicate the value and benefits of upgrading, offering incentives such as discounts or limited-time offers. Gradually introduce premium features or additional support to enhance the paid experience.
Provide clear upgrade paths and highlight success stories or testimonials from paying customers. Maintain transparency about pricing and changes, and continue engaging free users through targeted messaging and personalized support to build trust and encourage upgrades.
Requiring credit card information upfront for a free trial can deter potential users who are hesitant to commit financially. It may lead to lower trial sign-up rates and limit user acquisition. Users may feel pressured to make a purchasing decision quickly, resulting in lower conversion rates if they don’t fully experience the product’s value.
To mitigate these risks, consider offering a trial without upfront credit card requirements, providing clear communication about trial terms, and ensuring a seamless cancellation process to build trust and encourage exploration.
Deciding the optimal length for a free trial period depends on the complexity of the product and the time users need to experience its value. For simple products with immediate value, a shorter trial period (7-14 days) may suffice.
More complex products may require longer trials (21-30 days) to allow users to explore features and achieve the “aha moment.” Analyze user feedback and behavior during the trial to identify when users typically experience value, and adjust the trial length accordingly to maximize conversions and user satisfaction.
The choice of pricing model impacts long-term growth and scalability by influencing customer acquisition, retention, and revenue generation. Freemium models can drive large-scale user acquisition and brand awareness, leading to organic growth. However, sustaining a large free user base may require significant resources.
Free trial models focus on quick conversions and revenue generation, providing a more predictable growth path. The choice of model should align with business goals, target market, and resource capacity to ensure sustainable growth and scalability in the competitive SaaS landscape.


